Talk with Your Graph Database: Natural Language Queries with FalkorDB and Text-to-Cypher
This project combines FalkorDB, a blazing-fast in-memory graph database, its web-based graph browser, and a powerful Text-to-Cypher application that allows you to query your graph database using free-text natural language queries. The answers you receive are also in natural language, lowering the barrier to interact with complex graph data.
All code is open source, with a link to the GitHub repository.
Overview
What is FalkorDB?
FalkorDB is a high-performance graph database designed to store and query complex relationships and entities efficiently. It supports the Redis protocol, allowing easy integration with existing Redis clients, and uses the Cypher query language to manipulate graph data.
What is Text-to-Cypher?
Text-to-Cypher is an application that connects to the FalkorDB graph database to enable users to ask questions in natural language and receive answers grounded in graph data. Instead of requiring knowledge of the Cypher query language (used to query property graphs), users simply express their questions in free text, and the system translates them into executable Cypher queries to retrieve corresponding information from the graph.
Text-to-Cypher provides two main interfaces for this:
-
A direct REST API that clients can call to submit natural language queries. This API returns progress updates as Server-Sent Events (SSE), allowing clients to receive incremental feedback about schema discovery, query generation, execution, and final results.
-
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, which hosts the Text-to-Cypher tool and exposes resources representing each graph in the FalkorDB database. MCP provides a standardized interface enabling integration with in-house or third-party MCP-compatible tools and AI assistants.
The advantage of the REST API interface is that it offers tight control and easy integration with existing or legacy software systems that prefer RESTful services and want granular SSE progress updates.
The MCP server, on the other hand, excels in environments where multiple AI assistants or tools interact collaboratively. MCP enables seamless integration, resource discovery, and invocation of the Text-to-Cypher tool alongside other graph-related capabilities, allowing flexible multi-service ecosystems.
With Text-to-Cypher connected to FalkorDB, users and applications can ask complex, multi-hop questions about an organization’s knowledge graph—unlocking insights without writing raw Cypher queries.
How It Works
-
Accepting User Free Text Query: The system accepts a natural language query from the user, optionally including conversational history for context.
-
Generating Schema for the Graph: It retrieves the graph schema (node labels, relationships, properties) from FalkorDB and caches it for efficiency.
-
Generating Cypher Query: Using the user input and cached schema, the system leverages AI to translate the natural language query into an executable Cypher query.
-
Executing the Cypher Query: The generated query is executed against the FalkorDB graph database.
-
Returning Free Text Answer: Finally, the system uses both the original user query and the Cypher query results to compose and return a natural language answer.
How to use it
Running the Services with Docker
The app is written in the Rust programmng langauge and you can build it from source on your machine or use pre built release
You can run the entire stack easily using Docker. This includes:
- FalkorDB Graph Database (port 6379)
- Graph Browser Web Interface (port 3000)
- Text-to-Cypher API for natural language query translation (port 8080)
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server for AI assistant integrations (port 3001)
Example command:
docker run -p 6379:6379 -p 3000:3000 -p 8080:8080 -p 3001:3001 \
-v $(pwd)/.env:/app/.env:ro falkordb/text-to-cypher
Your .env file should contain the AI model and key configurations, for example:
DEFAULT_MODEL=gpt-4
DEFAULT_KEY=your-api-key-here
Loading Example Data
You can load a sample social network graph using the included bash script with redis-cli. This creates people nodes and friend relationships.
#!/usr/bin/env bash
GRAPH_NAME="social"
# Create nodes
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "CREATE
(p1:Person {name: 'Alice'}),
(p2:Person {name: 'Bob'}),
(p3:Person {name: 'Carol'}),
(p4:Person {name: 'David'}),
(p5:Person {name: 'Eve'}),
(p6:Person {name: 'Frank'}),
(p7:Person {name: 'Grace'}),
(p8:Person {name: 'Heidi'}),
(p9:Person {name: 'Ivan'}),
(p10:Person {name: 'Judy'})"
# Create relationships
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p1:Person {name: 'Alice'}), (p2:Person {name: 'Bob'}) CREATE (p1)-[:FRIEND]->(p2)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p2:Person {name: 'Bob'}), (p3:Person {name: 'Carol'}) CREATE (p2)-[:FRIEND]->(p3)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p3:Person {name: 'Carol'}), (p4:Person {name: 'David'}) CREATE (p3)-[:FRIEND]->(p4)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p4:Person {name: 'David'}), (p5:Person {name: 'Eve'}) CREATE (p4)-[:FRIEND]->(p5)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p5:Person {name: 'Eve'}), (p6:Person {name: 'Frank'}) CREATE (p5)-[:FRIEND]->(p6)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p6:Person {name: 'Frank'}), (p7:Person {name: 'Grace'}) CREATE (p6)-[:FRIEND]->(p7)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p7:Person {name: 'Grace'}), (p8:Person {name: 'Heidi'}) CREATE (p7)-[:FRIEND]->(p8)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p8:Person {name: 'Heidi'}), (p9:Person {name: 'Ivan'}) CREATE (p8)-[:FRIEND]->(p9)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p9:Person {name: 'Ivan'}), (p10:Person {name: 'Judy'}) CREATE (p9)-[:FRIEND]->(p10)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p10:Person {name: 'Judy'}), (p1:Person {name: 'Alice'}) CREATE (p10)-[:FRIEND]->(p1)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p1:Person {name: 'Alice'}), (p5:Person {name: 'Eve'}) CREATE (p1)-[:FRIEND]->(p5)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p2:Person {name: 'Bob'}), (p6:Person {name: 'Frank'}) CREATE (p2)-[:FRIEND]->(p6)"
redis-cli GRAPH.QUERY "$GRAPH_NAME" "MATCH (p3:Person {name: 'Carol'}), (p7:Person {name: 'Grace'}) CREATE (p3)-[:FRIEND]->(p7)"
This creates a connected network of people with friend relationships, perfect for testing queries.
Querying the Graph
You can query the graph through several interfaces:
- Web UI: Use the browser at
http://localhost:3000to visually explore and query the graph. - Text-to-Cypher API: Send natural language queries via REST API at
http://localhost:8080. - OpenAPI Swagger UI: Explore and execute API calls interactively at
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui/. - MCP Server: Integrate with AI assistants that use the Model Context Protocol on port 3001.
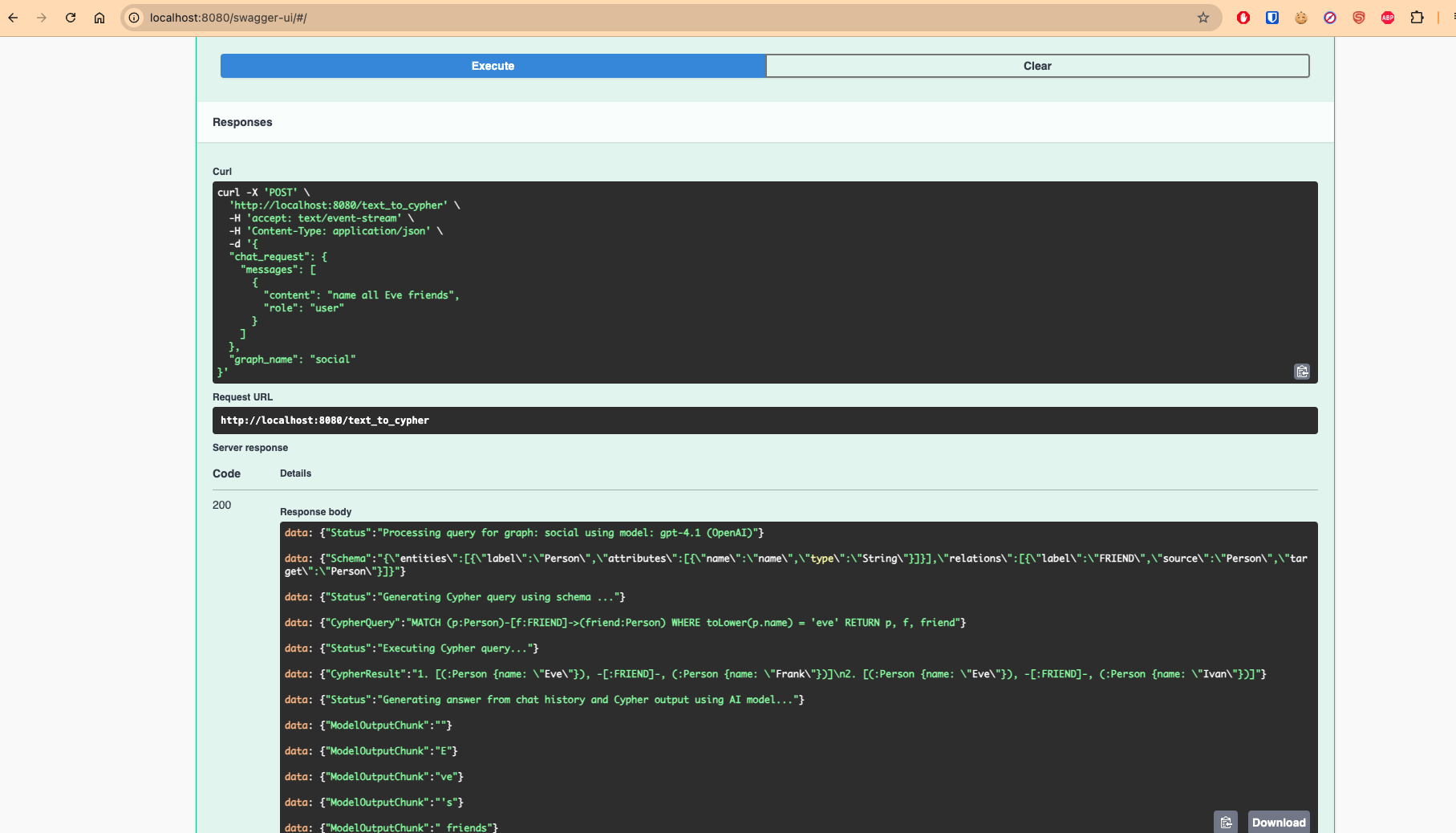
Example curl call to get a list of Eve’s friends:
curl -N --http2 -H "Accept:text/event-stream" -X 'POST' \
'http://localhost:8080/text_to_cypher' \
-H 'accept: text/event-stream' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"chat_request": {
"messages": [
{
"content": "name 3 of Eve friend",
"role": "user"
}
]
},
"graph_name": "social"
}'
This returns a streaming response with the Cypher query, execution results, and a natural language answer.
Concepts Explained
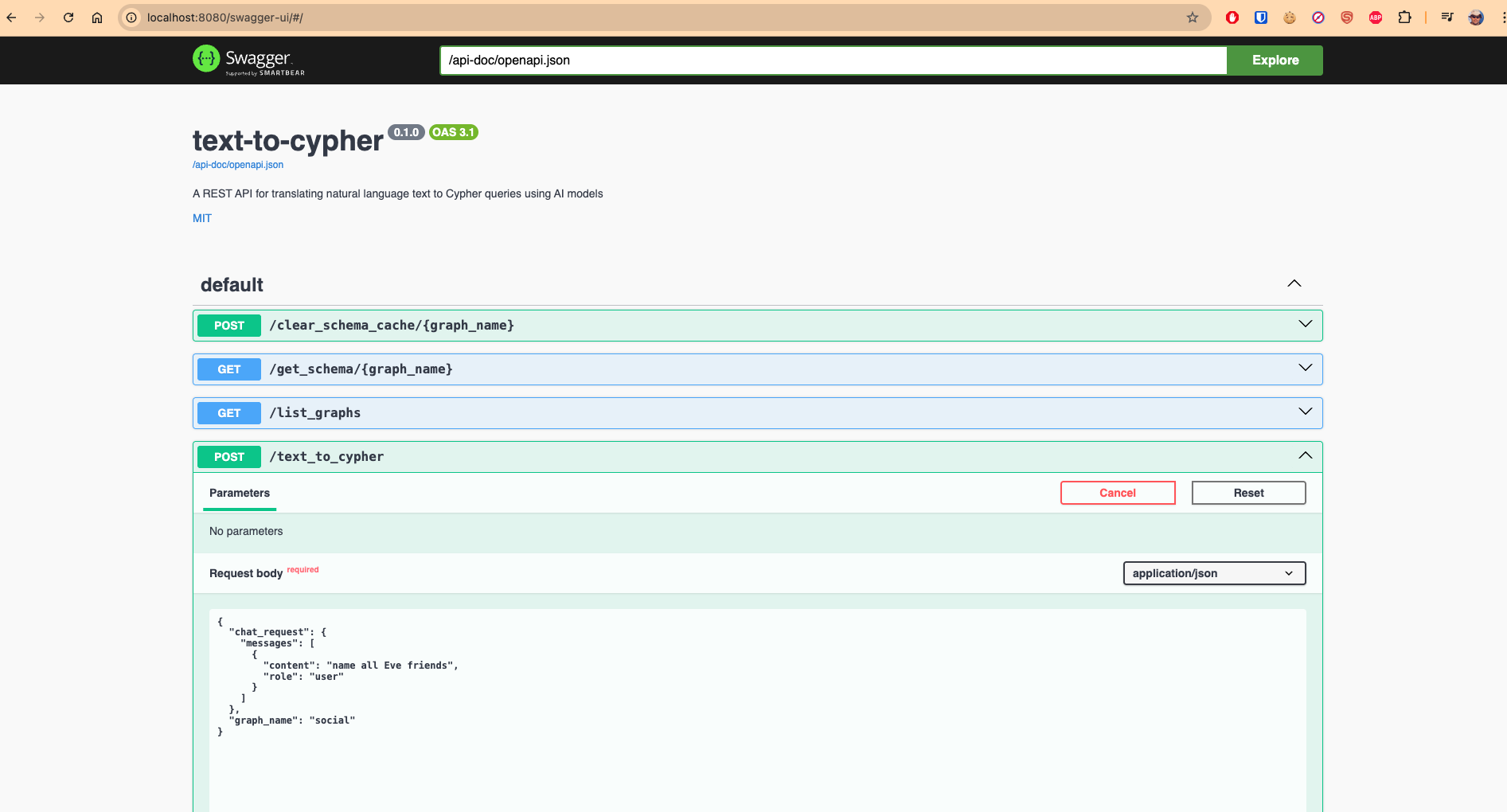
OpenAPI
OpenAPI is a widely-adopted specification for describing RESTful APIs in a machine-readable format. This allows automatic generation of documentation, client SDKs, and interactive tools like Swagger UI. In this project, the Text-to-Cypher API fully supports OpenAPI, making it easy for developers to discover and test endpoints.
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server
MCP provides a standardized way for AI assistants and tools to interact with APIs and data sources. It supports:
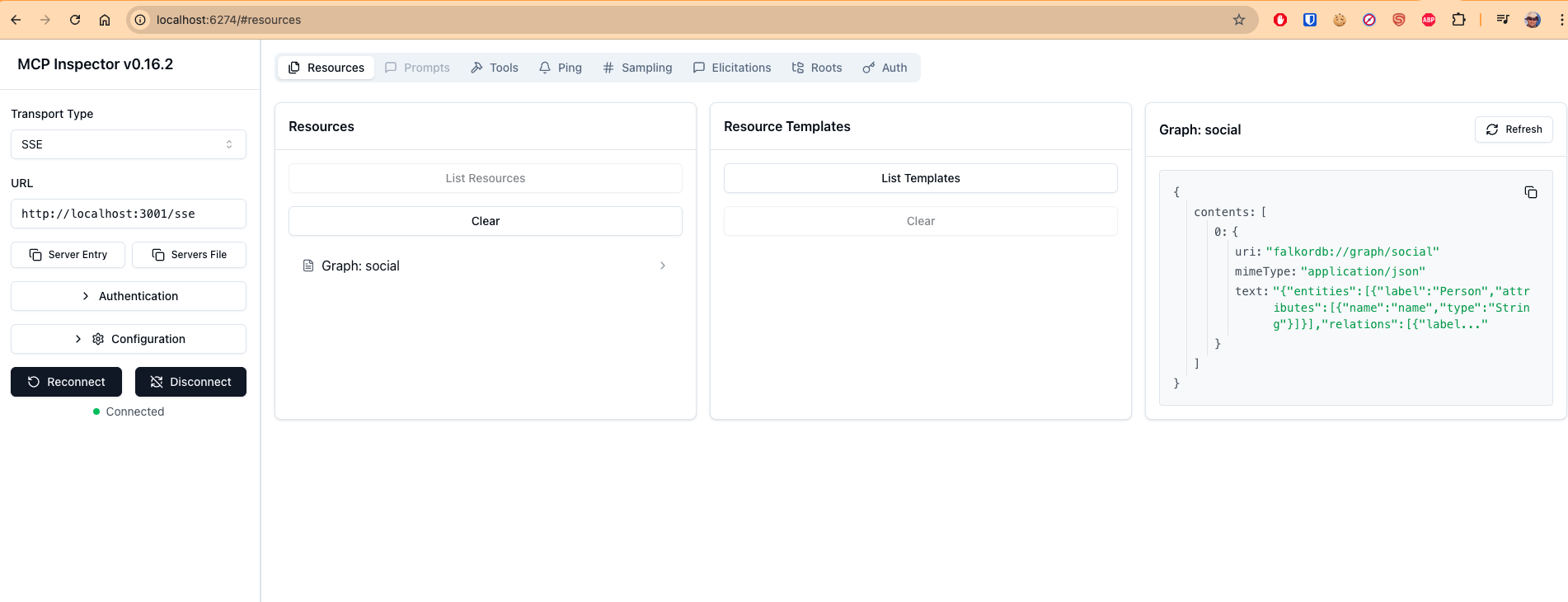
- Listing available graph resources and their schemas
- Listing and calling tools (like
text_to_cypher) - Streaming responses via Server-Sent Events (SSE)
You can connect to MCP using the MCP Inspector tool (npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/inspector):
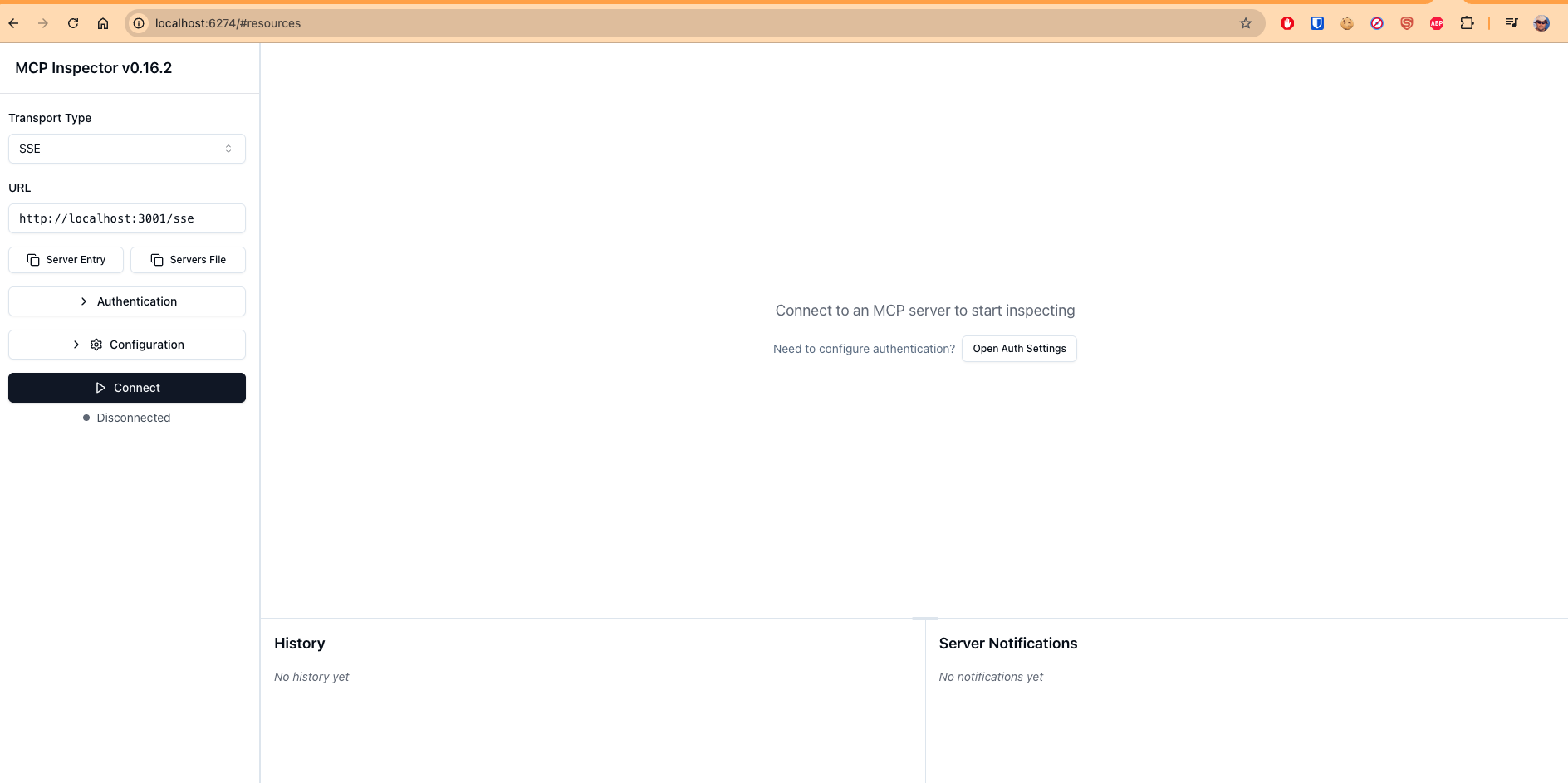
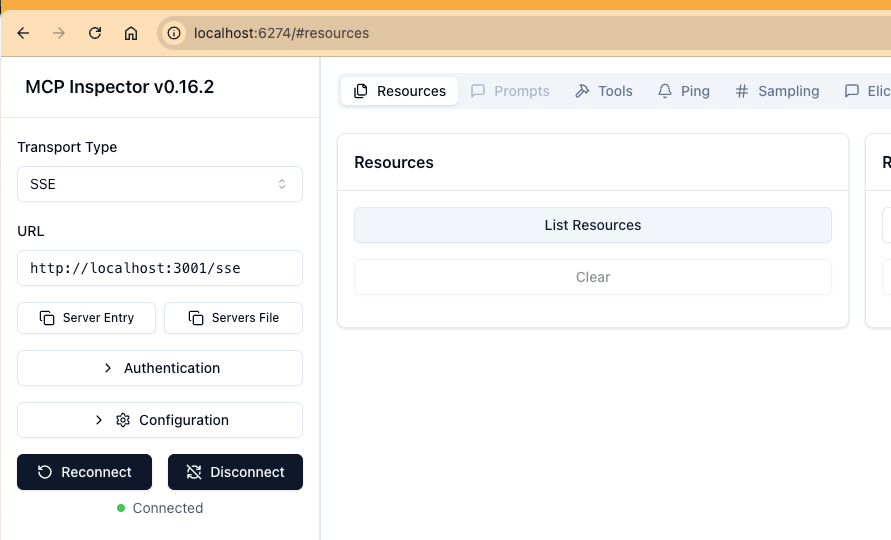
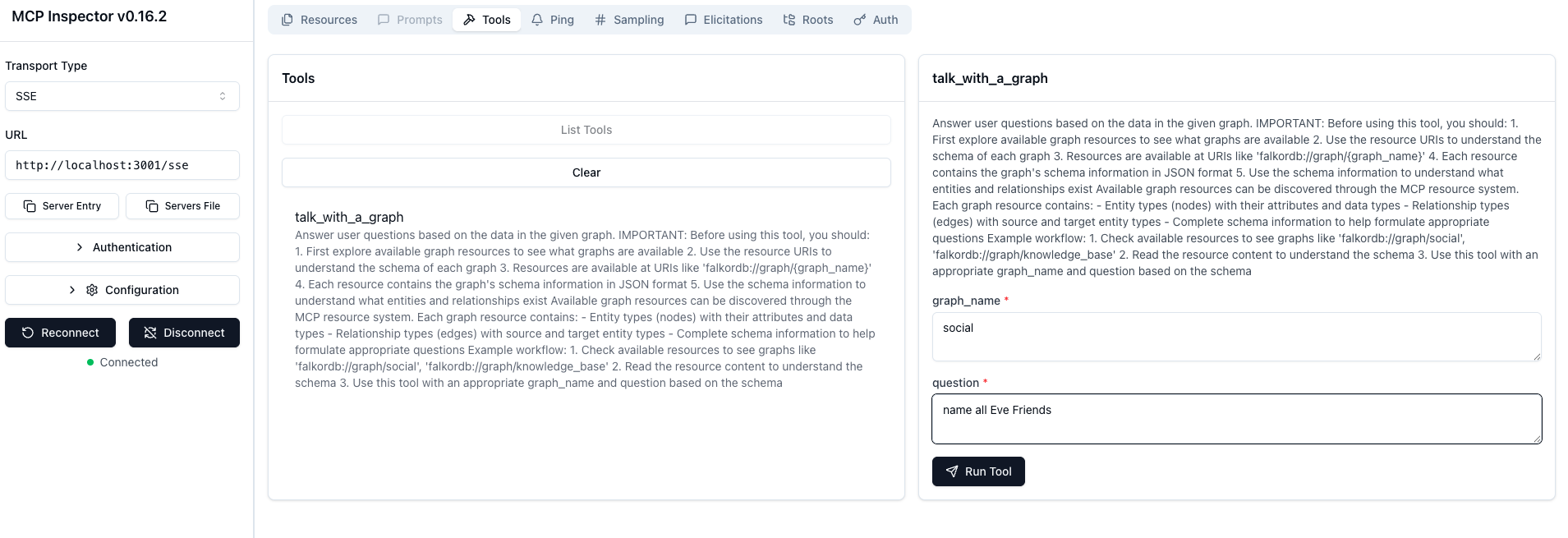
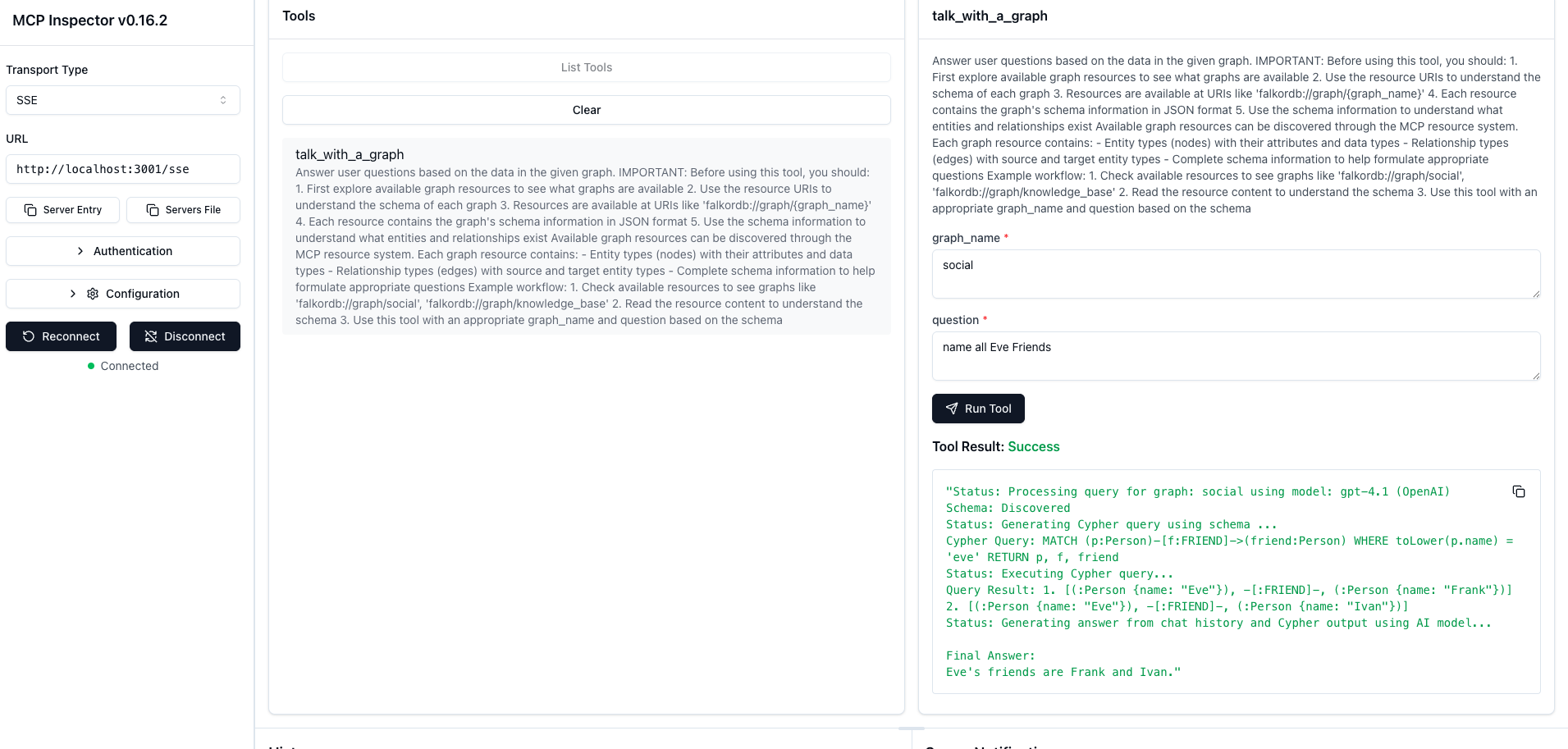
The inspector aggregates streamed events to display the complete response easily.
Using MCP you can configure text to cypher to be used from Claude destkop or vscode
Integration with Developer Tools and AI Platforms
Using MCP Server with Visual Studio Code
Configure VSCode to connect to the MCP server by adding a configuration file .vscode/mcp.json:
{
"servers": {
"talk_with_a_graph": {
"type": "sse",
"url": "http://localhost:3001/sse"
}
}
}
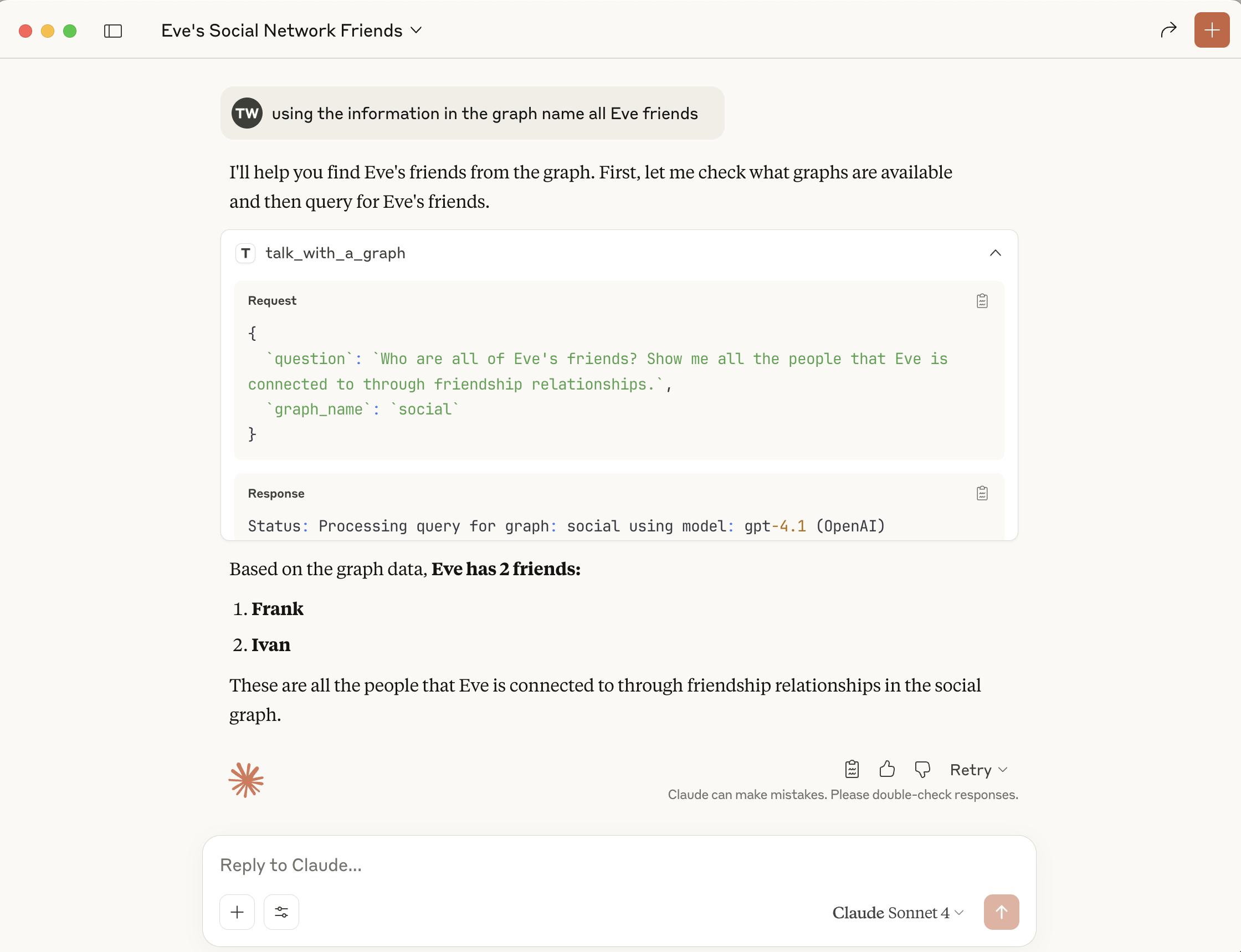
you can now ask: using the information in the graph list all Eve friends
Note that you do not have to name the graph name because the model use the mcp resources to find the right graph.
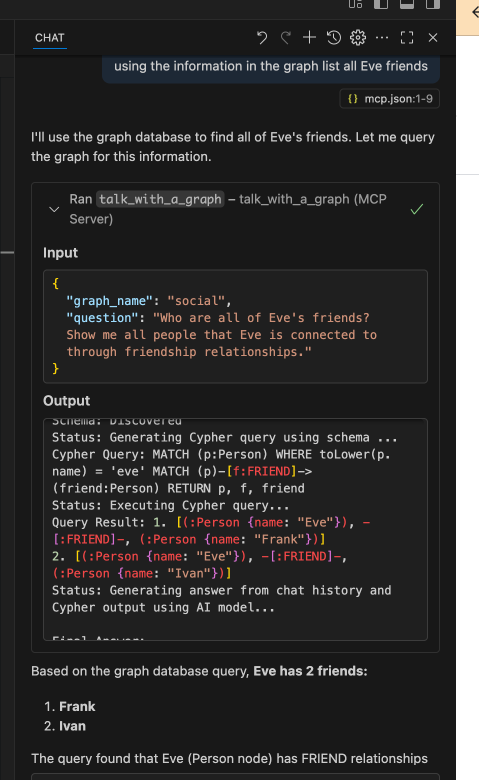
Another option is to add this MCP server to claude desktop
you can do that by add the file laude_desktop_config.json to /Users/$USER/Library/Application Support/Claude with this content:
{
"mcpServers": {
"talk_with_a_graph": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"mcp-remote",
"http://localhost:3001/sse"
]
}
}
}
Note the claude destop does not stream the SSE event to the user (it buffer the events)
Server-Sent Events (SSE)
SSE is a protocol that allows servers to push real-time updates to clients over HTTP. Here, SSE is used to stream progressive query processing updates, including:
- Status messages
- Schema discovery
- Cypher query generation
- Query execution results
- Final natural language answers
This real-time feedback improves user experience, especially for longer or complex queries.
Potential Use Cases
- Enterprise Knowledge Management: Allow employees to query corporate knowledge graphs without knowing query languages.
- Customer Support: AI assistants leverage organizational data to answer customer queries effectively.
- Research Data Exploration: Academics explore complex relationships in research datasets intuitively.
- Intelligent Chatbots: Integrate graph-backed insights into conversational AI for enriched responses.
- Custom Analytics Dashboards: Use natural language queries to build dynamic graph visualizations and reports.
What Can Be Built on Top?
- Advanced AI Assistants that integrate multiple data sources and provide context-aware recommendations.
- Automated Data Governance Tools that analyze relationships and data lineage interactively.
- Collaboration Platforms where users query and discuss data insights leveraging the knowledge graph.
- Domain-Specific Query Builders which optimize natural language understanding for specialized vocabularies.
Resources
- GitHub repository: https://github.com/FalkorDB/text-to-cypher
- MCP Inspector:
npx -y @modelcontextprotocol/inspector
Feel free to explore and contribute to this open-source ecosystem, bringing your organization’s local knowledge graph interaction to the next level!